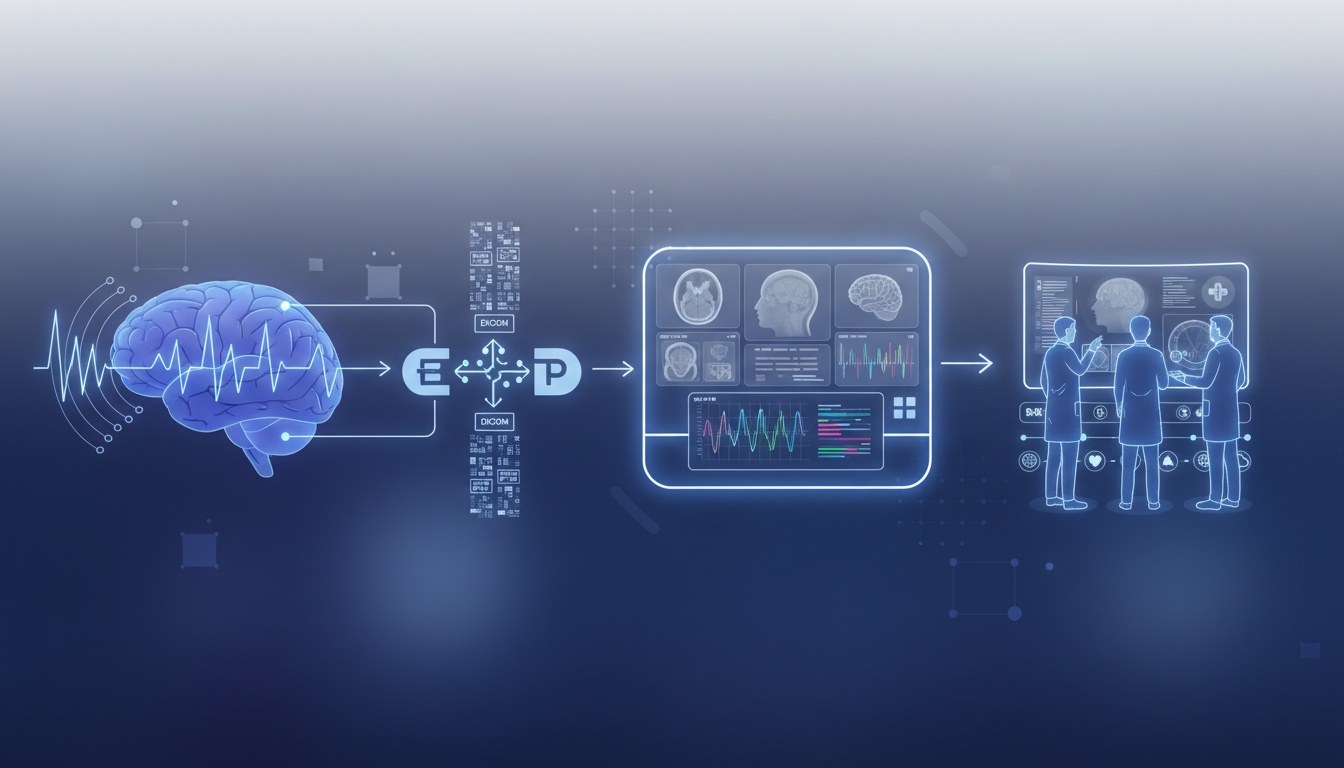

Electroencephalography (EEG) is pivotal in neurological diagnosis and monitoring, offering insights crucial for understanding various brain conditions. However, the full potential of EEG can only be realized when integrated effectively with other diagnostic tools.
This is where the integration of EEG with PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) becomes transformative. PACS is traditionally celebrated for its robust handling and archiving of imaging data. Still, its potential to manage EEG data alongside images like MRI or CT scans can elevate diagnostic precision and patient care to new heights.
This blog explores how merging EEG data into PACS systems streamlines workflows and enhances medical professionals' collaborative efforts in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders.
Join us as we delve into the benefits, challenges, and solutions for integrating these vital technologies in healthcare.
Electroencephalography (EEG) and Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) are two pillars of modern medical diagnostics, each serving distinct but potentially complementary roles in healthcare.
EEG is a method for recording brain electrical activity. Through electrodes placed on the scalp, EEG captures fluctuations in brain activity that can be crucial for diagnosing and monitoring neurological disorders such as epilepsy, brain tumors, and sleep disorders.
This technology is particularly valued for its high temporal resolution, which helps in tracking brain dynamics at the millisecond level, something not possible with most imaging techniques.
PACS refers to systems designed primarily for storing, retrieving, managing, and sharing medical images within a healthcare institution.
These systems integrate various imaging modalities, like MRI and CT scans, providing a centralized repository that improves access to data and facilitates efficient healthcare delivery. PACS supports radiology departments and extends to other medical fields needing imaging services.
While PACS was traditionally used for imaging data, its framework is increasingly adapted to include non-imaging diagnostic data such as EEG. This integration is facilitated by DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) standards, which have evolved to encompass not only traditional images but also structured data and waveforms like those produced by EEG.
Integrating EEG into PACS involves several key steps:
Standardization of EEG Data: Converting EEG data into a DICOM-compatible format ensures it can be effectively stored and managed within a PACS. This process often includes encapsulating raw EEG data and relevant metadata like patient information and clinical context.
Enhanced Data Access and Collaboration: By incorporating EEG into PACS, neurologists, and other specialists can access a patient’s diagnostic data alongside imaging studies, improving diagnostic accuracy and facilitating more comprehensive treatment planning.
Streamlined Workflow: Having EEG data in PACS can streamline workflows, allowing for easier data management, better security, and compliance with health data regulations. It simplifies the medical staff process by providing a unified system for accessing patient information.
The integration of EEG into PACS represents a significant advancement in medical diagnostics, allowing for more unified patient profiles and supporting more informed clinical decisions. As medical technology continues to evolve, the ability of PACS systems to incorporate a broader range of diagnostic data will be crucial in enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of medical care.
Integrating EEG data into Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) presents several significant advantages that can transform the efficiency and effectiveness of medical diagnostics in healthcare facilities.
Combining EEG and other diagnostic data within PACS simplifies and streamlines workflows throughout the medical facility. Centralized data management means all patient information, including EEG waveforms, imaging studies, and other diagnostic results, is stored in a single, accessible system. This consolidation eliminates the redundancies and delays typically occur when data is scattered across multiple platforms or stored in disparate systems.
Medical staff can quickly and efficiently retrieve complete patient records—including historical and current EEG data—which is crucial for timely and effective patient care.
The integration of EEG data into PACS significantly impacts diagnostic accuracy. Specialists can make more informed decisions by having comprehensive access to both imaging and EEG data in one interface.
For example, neurologists reviewing EEG data can easily cross-reference MRI or CT scans available in the same system to better understand the patient’s condition.
This holistic view helps pinpoint diagnoses with greater precision, particularly in complex cases involving neurological disorders where multiple types of diagnostic data need to be correlated.
One of the most profound benefits of integrating EEG with PACS is enhancing interdisciplinary collaboration. In complex clinical environments, different specialists—such as neurologists, radiologists, and neurosurgeons—often need to work together to develop an effective treatment plan.
A shared PACS platform allows all relevant specialists to access and review diagnostic data, including EEG, without needing separate meetings or disparate data-sharing practices. This capability ensures that all team members have a unified understanding of the patient's condition, leading to more coordinated care planning and potentially better patient outcomes.
Integrating EEG data into a PACS environment is a complex process that requires understanding both the technical standards and the practical requirements of the systems involved.
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is the universal standard for handling, storing, and transmitting information in medical imaging. It includes supplements that specifically address the storage and communication of EEG data.
Supplement 30 of the DICOM standard deals with waveforms and is particularly relevant. This supplement outlines how to encapsulate waveform data, like those generated by EEG devices, within a DICOM format.
This standardization ensures that EEG data can be integrated into PACS, allowing it to be accessed and reviewed alongside other imaging data like MRIs or CT scans. Thus, it provides a holistic view of a patient's diagnostic information.
Integrating EEG into an existing PACS system requires careful consideration of both hardware and software needs:
Hardware Requirements: Adequate storage and robust processing power are necessary to handle the large data sets associated with EEG data, especially when dealing with high-frequency recordings. The PACS server must be capable of managing high data throughput to ensure efficient data retrieval and storage without lag.
Software Requirements: The PACS software must be compatible with the DICOM standards for waveform data and capable of interpreting the specific data encapsulation used for EEG waveforms. Many PACS systems require additional plugins or updates to handle EEG data seamlessly.
Integrating EEG data into PACS also challenges data security and regulatory compliance. EEG data is sensitive and subject to the same compliance standards as other types of medical data, such as HIPAA in the United States:
Encryption: Data must be encrypted at rest and during transmission to protect patient privacy and ensure unauthorized entities cannot access the data.
Access Controls: Proper access controls must be implemented to ensure that only authorized personnel can access EEG data. This includes using secure login mechanisms and maintaining detailed access logs.
Audit Trails: It is crucial for compliance to keep detailed logs of who accessed the EEG data and when. Audit trails help track data usage and identify potential security breaches or non-compliance with regulatory standards.
Integrating EEG data into PACS systems presents several challenges that healthcare facilities must navigate. These challenges range from technical compatibility issues to staff training needs and budget considerations.
Understanding these challenges and identifying effective solutions is essential for a successful integration.
Challenge: One of the primary hurdles in integrating EEG with PACS is ensuring that both systems are technically compatible. Many PACS systems are primarily designed to handle image data and may only support the waveform data produced by EEG with modifications.
Solution: To overcome compatibility issues, working with PACS and EEG vendors is crucial to ensure that both systems communicate effectively. This might involve upgrading the PACS software to support EEG data formats or using middleware that can translate EEG data into a format the PACS can handle. Regular software updates and choosing vendors that comply with the latest DICOM standards can also help mitigate these issues.
Challenge: Successfully integrating EEG data into PACS requires adequately trained staff across multiple departments. This includes radiologists, technicians, and IT staff who manage the PACS system.
Solution: Comprehensive training programs are essential. These programs should cover the technical aspects of the EEG and PACS systems, focusing on accessing and interpreting EEG data within the PACS. Additionally, regular refresher courses and access to ongoing support from system vendors can help staff stay updated on new features and best practices.
Challenge: Integrating EEG into PACS often involves significant initial costs, including software upgrades, potential hardware enhancements, and training programs. Additionally, system maintenance and updates have ongoing costs.
Solution: Careful budgeting is crucial. Facilities should conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis to understand the potential return on investment (ROI) that EEG-PACS integration can offer. Considerations might include improved diagnostic accuracy, more efficient patient throughput, and reduced reliance on multiple systems. Facilities may also explore various financing options or grants for technology upgrades in healthcare settings.
 - Created by PostDICOM.jpg)
Integrating EEG data into PACS systems is a pioneering step in medical technology, merging the realms of neurology with radiological imaging. This section delves into a real-world case study of a healthcare facility that successfully implemented this integration, alongside expert tips that could guide similar endeavors.
Background: A sizeable neurological center specializing in epilepsy and other neurological disorders faced significant challenges in managing diagnostic data scattered across multiple systems. Their EEG data was isolated from imaging studies, complicating the diagnostic process and delaying patient care.
Implementation: The center decided to integrate EEG data into its existing PACS, facilitating access to all diagnostic information in one place. The integration process involved updating the PACS software to handle EEG waveforms according to the DICOM standards and training staff on the new system functionalities.
Outcome: Post-integration, the center reported significantly improved diagnostic speed and accuracy. Neurologists could now quickly access correlated EEG and imaging data, enabling faster, more accurate assessments for epilepsy surgeries and other treatments. The unified system also enhanced collaborative efforts across departments, streamlining patient management and improving outcomes.
1. Comprehensive Planning: Before integration, conduct thorough planning involving all stakeholders, including IT specialists, neurologists, and radiologists. Detailed planning helps anticipate challenges and aligns the integration process with clinical goals.
2. Choose the Right Technology Partner:: Select a software provider experienced in imaging and waveform data. A knowledgeable partner can provide crucial support during and after the integration process.
3. Prioritize Training: Comprehensive training for all users is crucial. Ensure that everyone, from technicians to physicians, understands how to access and interpret the integrated data. Regular training sessions can help users adapt to system updates and new functionalities.
4. Regular System Evaluation: Continuously evaluate the system’s performance and user satisfaction. Regular feedback loops with users can help identify areas for improvement and ensure the system meets evolving clinical needs.
5. Focus on Data Security: Integrate strong security measures to protect patient data from the outset. Incorporate encryption, access controls, and audit trails to ensure compliance with health data regulations.
Integrating EEG data into PACS is more than just a technical upgrade; it's a strategic enhancement that transforms how healthcare facilities handle diagnostic data. This convergence empowers clinicians with a comprehensive view of patient information, leading to quicker, more accurate diagnoses and fostering a collaborative environment among medical specialists. The benefits of this integration extend beyond operational efficiency to directly improve patient outcomes.
For facilities aiming to lead in healthcare innovation, embracing this integration is crucial. Choosing the right partner for this journey is equally important. PostDICOM stands out as a leader in cloud PACS services, offering robust solutions that simplify the complex process of integrating EEG with PACS.
By partnering with PostDICOM, healthcare facilities can ensure a seamless, secure, and efficient integration, setting a new standard in patient care. Embrace the future of medical diagnostics with PostDICOM, where advanced technology meets clinical excellence.
|
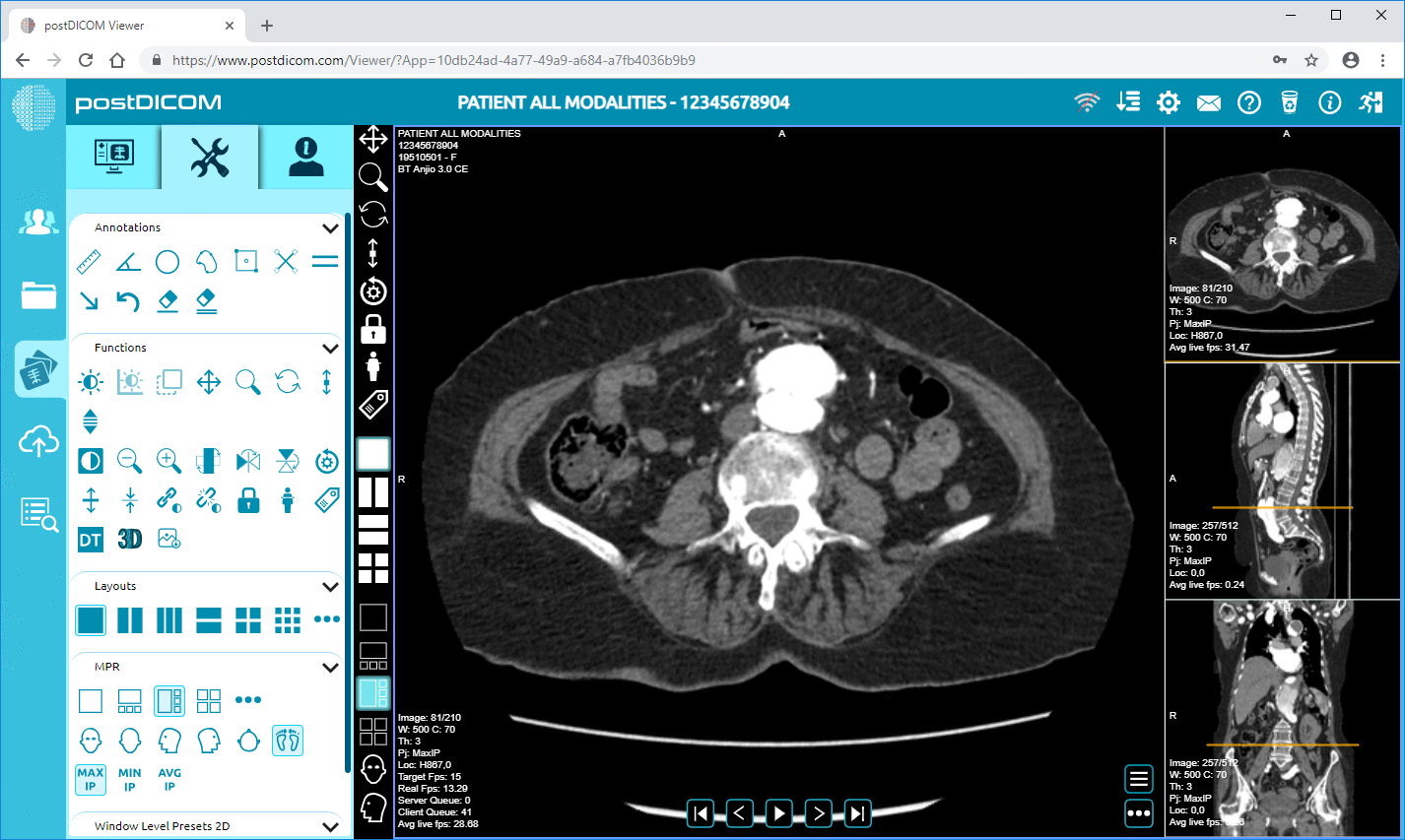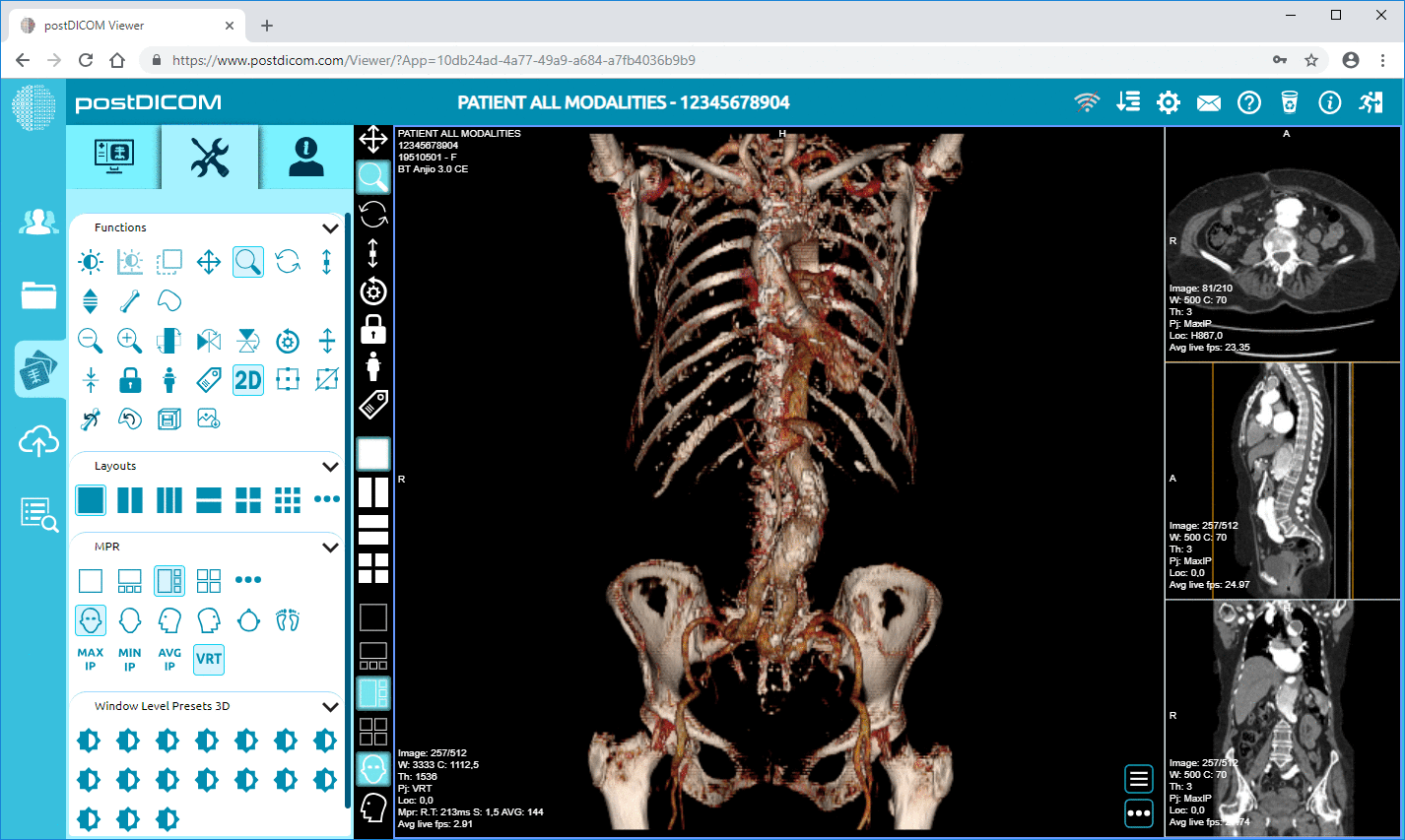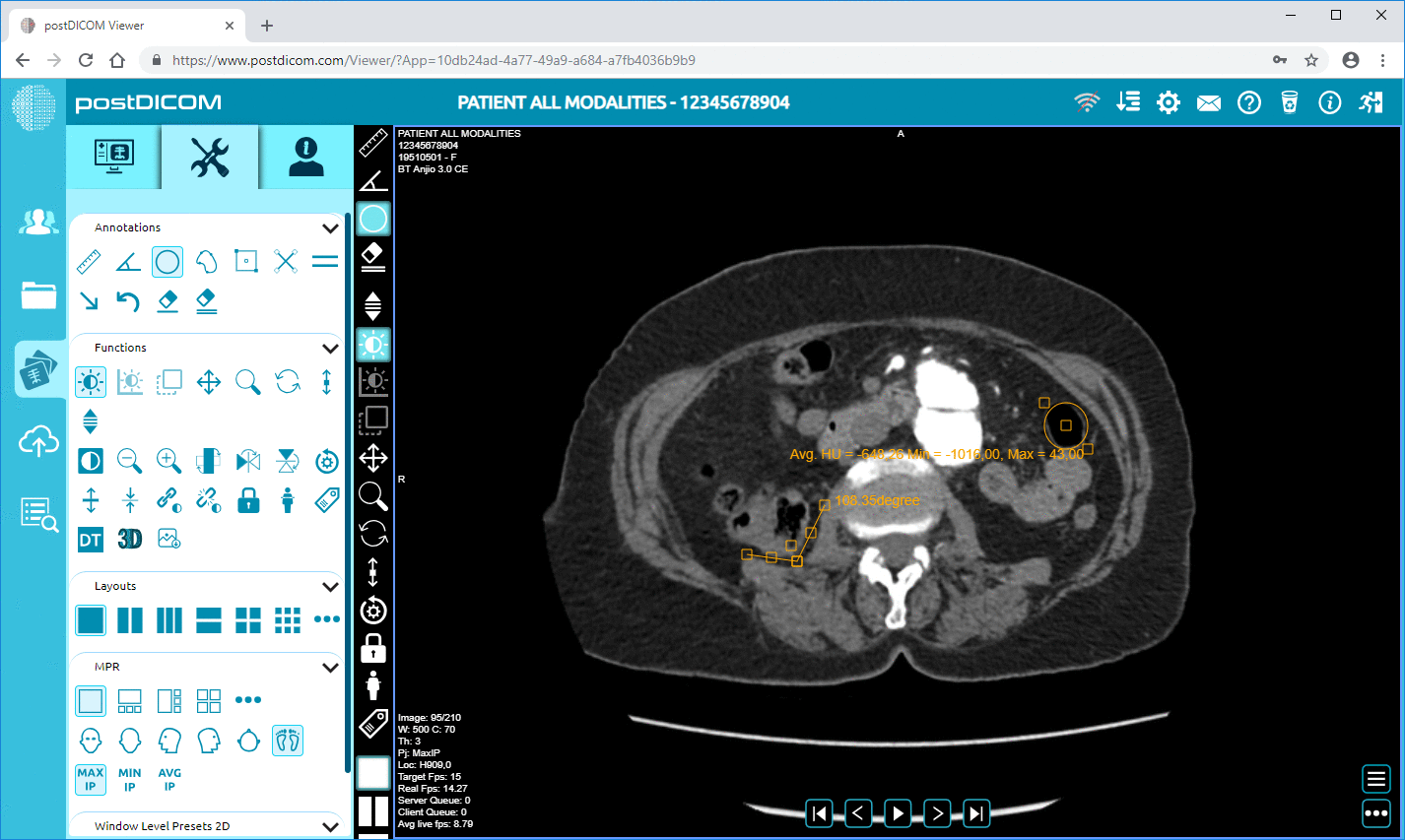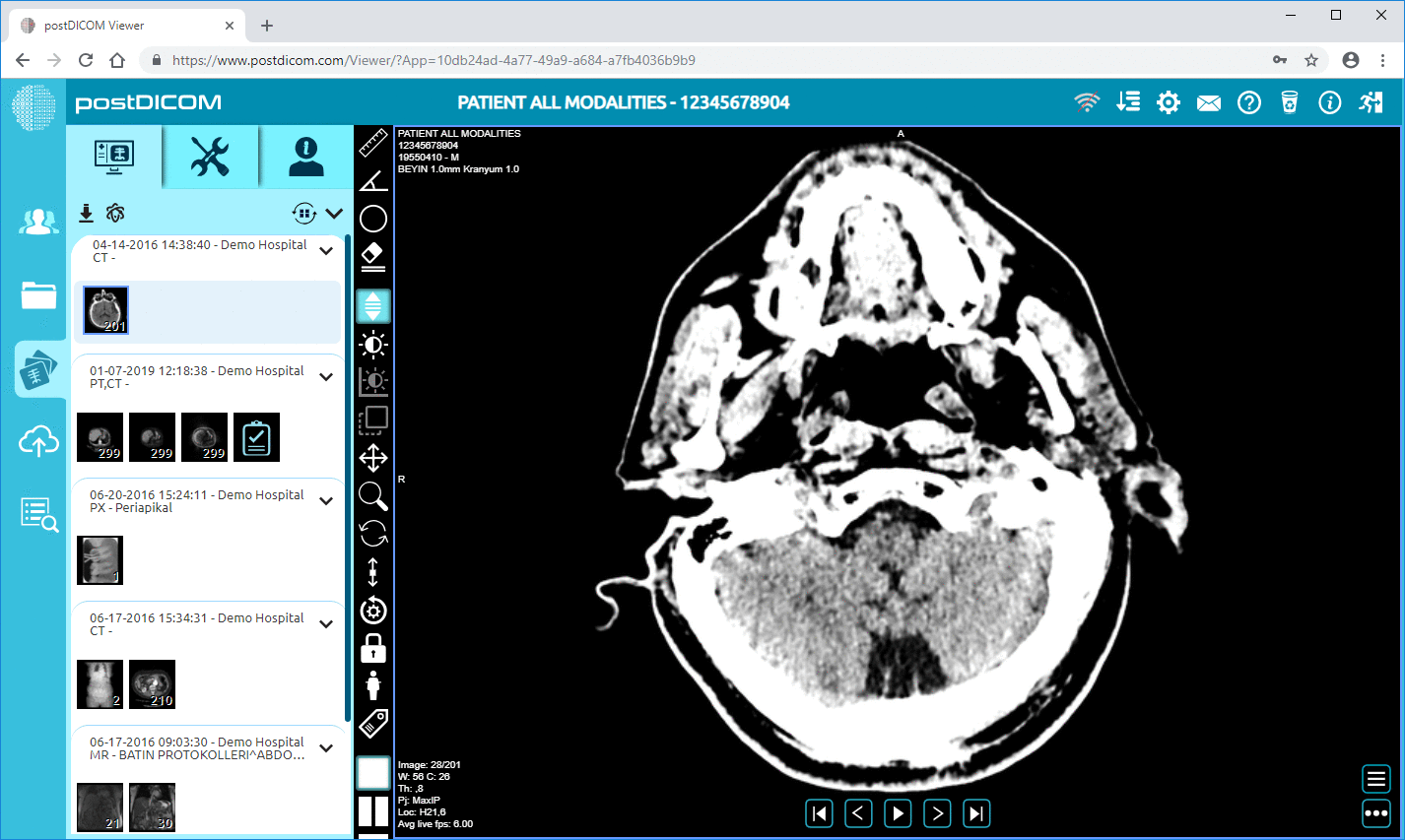
Cloud PACS and Online DICOM ViewerUpload DICOM images and clinical documents to PostDICOM servers. Store, view, collaborate, and share your medical imaging files. |